Chronic Venous Insufficiency
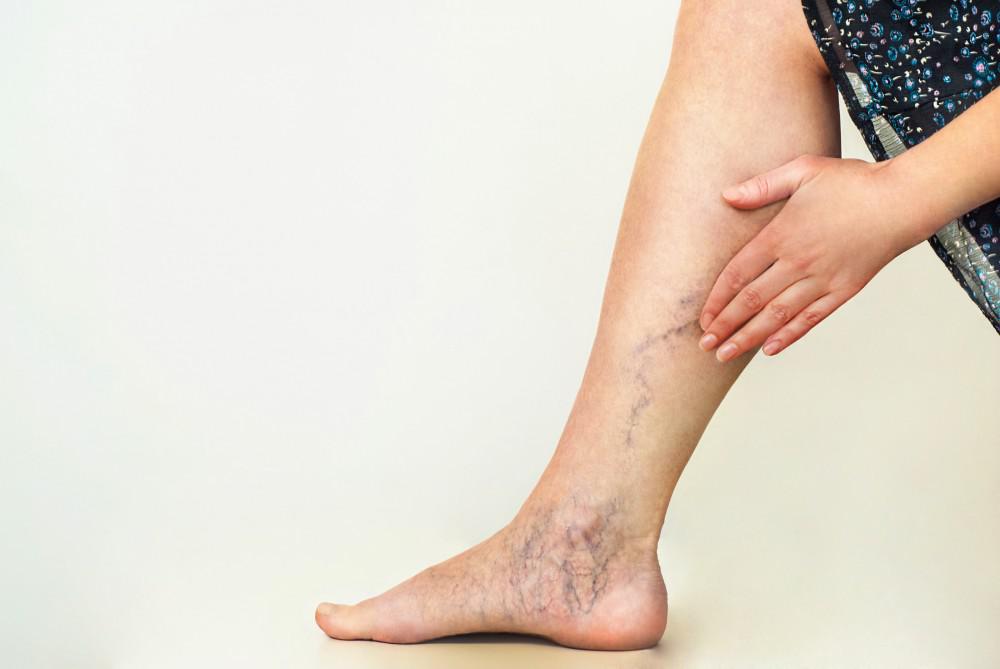
Introduction to Chronic Venous Insufficiency
Your arteries are pipes inside your body that carry blood from your heart to the rest of your body and your veins carry blood back to your heart from the rest of your body. Veins have one-way valves that prevent the blood from flowing backward, to ensure they reach your heart properly.
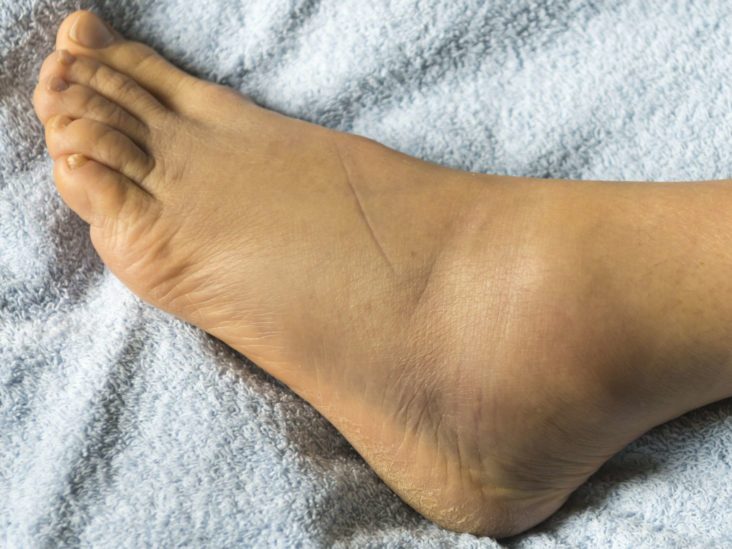
When your vein walls and valves are damaged, the veins cannot manage blood flow as well as they should and it is harder for blood in your legs to return to your heart. This causes a pool of blood in your legs and increases the pressure on the walls of the veins; this is known as chronic venous insufficiency.
Chronic venous insufficiency is most commonly caused by blood clots (deep vein thrombosis) and varicose veins. In some cases, weakened leg muscles have trouble squeezing blood upwards and can contribute to venous insufficiency.
Other risk factors include obesity, pregnancy, sitting or standing for long periods of time without moving, and family history of venous insufficiency.
What are the symptoms of venous insufficiency
- Swelling of the leg and ankle
- Itchiness of the legs
- Aching, throbbing, or heaviness of the legs
- Leg ulcers
- Pain that gets worse when you’re standing and gets better when you raise your legs (worse at night when sleeping)
- Skin changes especially around the ankle
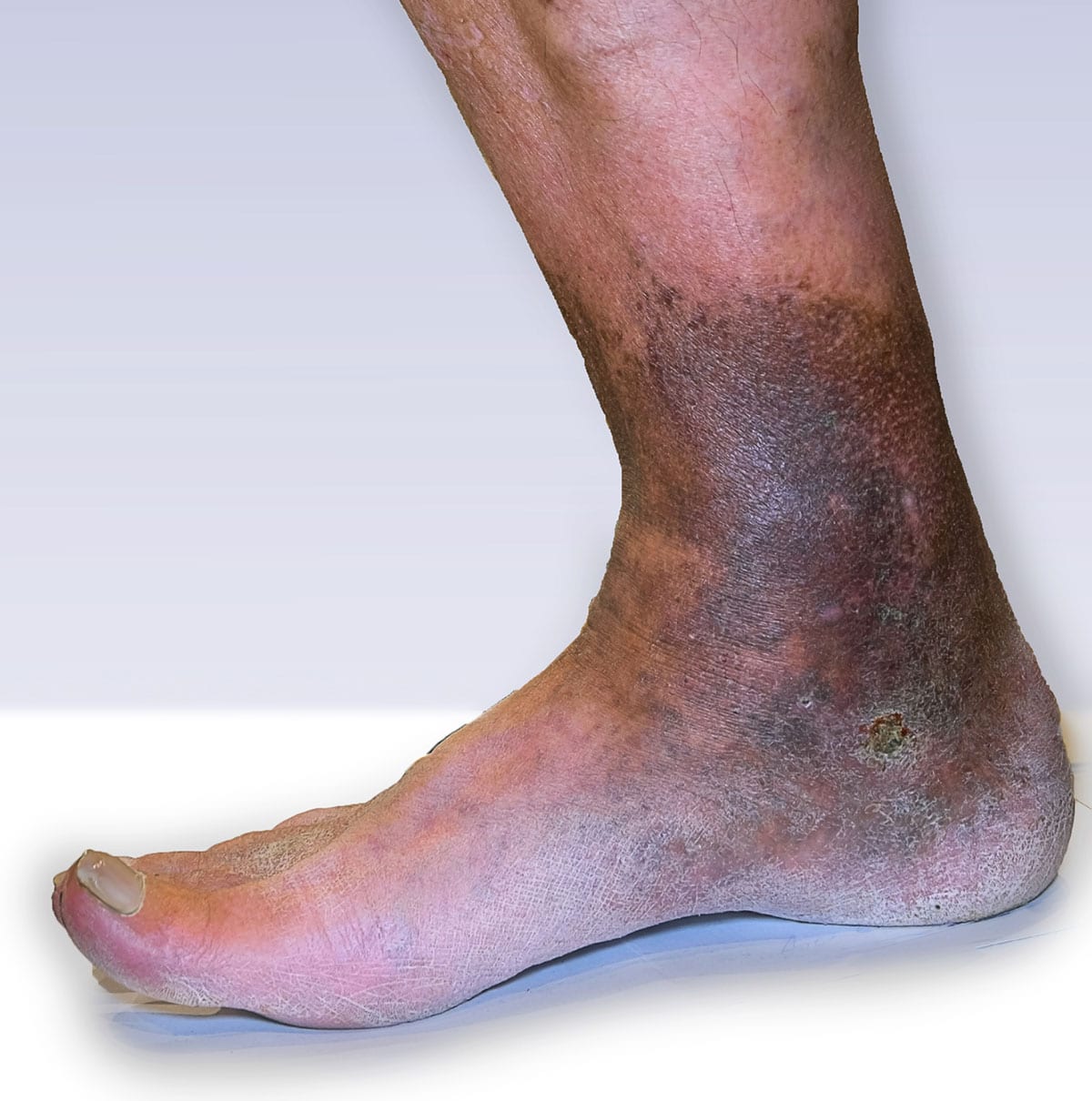
How to treat venous insufficiency
Without treatment, the pressure and swelling will burst the tiny blood vessels in your legs called capillaries. This can result in skin changes such as reddish brown discolouration especially near the ankles which can lead to swelling and ulcers. The below are some ways to treat and improve venous insufficiency at home:
- Wear compression stockings to help with your blood flow return and relieve symptoms
- Lifestyle changed such as exercise and diet to improve your blood flow
- Stop smoking to improve your blood flow
- Calf muscle movement while sitting or standing for long periods of time
- Maintain good skin care by moisturising daily
- Elevating calves when laying down or sitting down
- Calf raises to activate the muscle pump that helps the blood flow up to the heart
The above measures may not be sufficient in treating your condition, and seeking medical advise from your Doctor is the best way to treat and look after your venous insufficiency. It is also advisable to speak to your Podiatrist about your concerns.
The Foot Force Podiatry
Contact Us
Send us an e-mail:
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Ankle Instability
and Pain
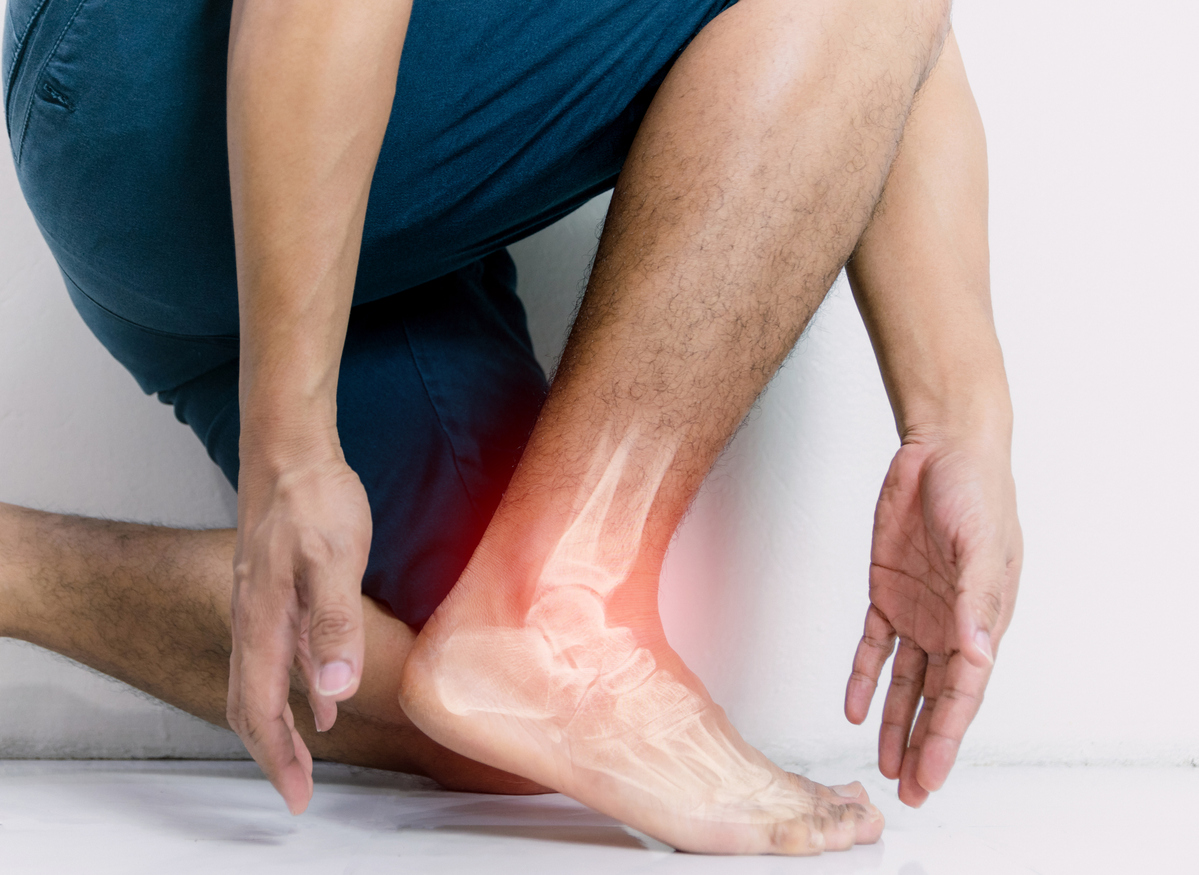
Ankle instability or ‘weak ankles’ is very common, especially when there has been a previous injury, such a sprain to the ankle. Weak ankles can affect balance and increase your risk of sprains which can lead to chronic ankle instability. Weak ankles can sometimes be caused by genetics, ligament laxity or even inappropriate footwear.
Chronic ankle instability is a condition characterized by ‘giving way’ of the outer side of the ankle. This condition often develops after repeated ankle sprains. Many athletes, as well as non-athletes, suffer from chronic ankle instability.
40% of people who suffer their FIRST ankle sprain will go on to suffer from chronic ankle instability within the first year since it has occurred. Inappropriate or inadequate ankle rehabilitation following an ankle sprain may result in chronic ankle instability.
There are many reasons why someone may have weak ankles. However, there are many things we can do to fix it!
What are the signs and symptoms of ankle instability?
- Repeated turning of the ankle, especially on uneven surfaces or when participating in sports
- Persistent discomfort and swelling
- Ankle pain or tenderness
- Ankle feeling wobbly or unstable (poor balance)
Treatment:
- RICER: Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation, Referral (to see a Podiatrist)
- Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication to help alleviate the pain and inflammation (temporarily)
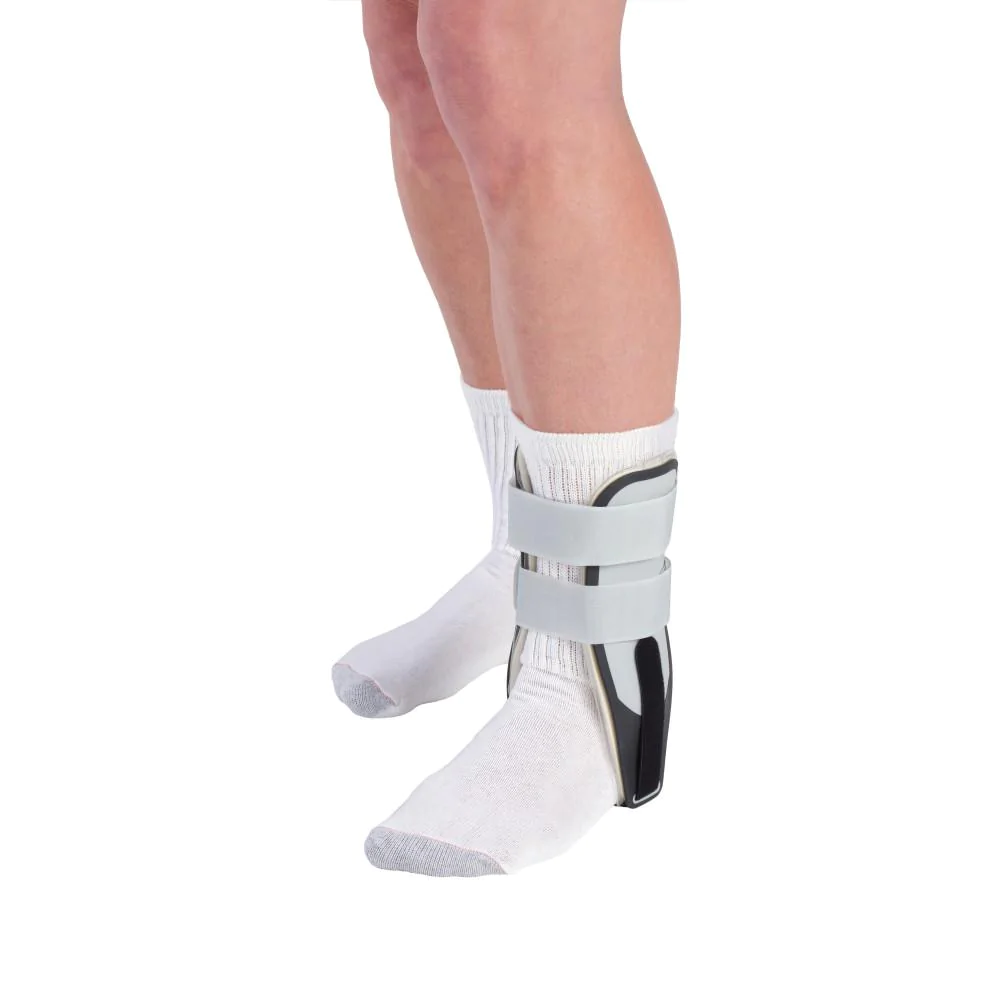
- Bracing: provide appropriate support to your ankle and prevent your ankle from turning. It also allows the injured area to heal properly while allowing you to remain mobile
- Ankle rehabilitation: to strengthen the ankle, improve balance and range of motion, and retrain your muscles – See a Podiatrist for efficient rehabilitation
- Foot mobilisation: to restore normal function of your joints and bones of the foot and ankle – See a Podiatrist for efficient ankle mobilisation treatment

Preventative Measures:
- Stretching exercises prior to commencing exercises
- Wear appropriate footwear; avoid high heels
- Be extra careful when doing exercises on uneven surfaces
- Do ankle strengthening exercises
- Seek a Podiatrist for more personalised advice and treatment
Here at the Foot Force Podiatry, we offer a range of treatment options to help with rehabilitation and prevention of ankle instability. Book your initial biomechanical assessment NOW!
Book OnlineContact Us
Send us an e-mail:
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
